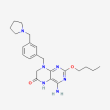
Drug information
| vesatolimod.mp3 |
C22 H30 N6 O2
4-amino-2-butoxy-8-[[3-(pyrrolidin-1-ylmethyl)phenyl]methyl]-5,7-dihydropteridin-6-one
Vesatolimod is in Phase 2a development for HIV treatment.
(Compound details obtained from PubChem,1 Gilead Sciences website,2 Clinical Infectious Diseases article,3 and ClinicalTrials.gov4,5)
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Immune modulator. Vesatolimod is a selective toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) agonist. It is an orally administered small molecule that works by binding to and activating TLR7, a pattern-recognition receptor (PRR) that is expressed primarily on plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) and B cells. PRRs are a key component of the innate host defense mechanism as they recognize and respond to infectious pathogens. As an immune modulator, vesatolimod may contribute to HIV control by triggering numerous inflammatory and immune responses, such as induction of interferon-stimulated gene expression and cytokine production, including type I interferon-alfa (IFN-alfa), as well as activation of natural killer (NK) cells, phagocytic cells, pDCs, and T cells.3,6–9
Vesatolimod’s potential role as a latency-reversing agent has also been evaluated in preclinical and clinical trials, with mixed results.3,6,7,10,11 Mechanistically, research has shown that the induction of HIV RNA by vesatolimod is dependent on IFN-alfa production by pDCs.6
Half-life (T½)
In a Phase 1b dose-escalation trial (NCT02858401) of vesatolimod (1 to 12 mg) administered orally every two weeks in adults with HIV who were virologically suppressed on ART, the vesatolimod median half-life ranged from 9 to 19 hours.3
Select Clinical Trials
Study Identifiers: A5374; NCT06071767
Sponsor: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
Phase: 1/2a
Status: This study is currently recruiting participants.
Study Purpose: The purpose of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of a combination regimen in adults who initiated suppressive ART during acute HIV infection. The combination regimen contains ChAdV- and MVA-vectored conserved mosaic T-cell vaccines, vesatolimod, and two broadly neutralizing antibodies (GS-5423 [also known as 3BNC117-LS] and GS-2872 [also known as 10-1074-LS]).
Study Population:
- Participants are adults with HIV who initiated ART within 28 days of acute HIV diagnosis and who have not interrupted ART for more than 14 consecutive days since initiation of ART.
- Participants have been receiving ART with an INSTI-based regimen with two NRTIs or a dolutegravir/lamivudine regimen for at least 6 weeks prior to study entry.
- Participants have HIV RNA <50 copies/mL since initial viral suppression on ART and for at least 1 year and within 60 days prior to study entry.
- Participants have CD4 counts ≥500 cells/mm3 within 60 days of study entry.12
Study Identifiers: AELIX-003; NCT04364035
Sponsor: Aelix Therapeutics
Phase: 2a
Status: This study has been completed.
Study Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of therapeutic HIV vaccines (HIVACAT T-cell immunogen [HTI] vaccines MVA.HTI and ChAdOx1.HTI) and vesatolimod in adults who had received early ART treatment.
Study Population:
- Participants were adults with HIV who had initiated ART within 6 months of HIV acquisition.
- Participants had HIV RNA <50 copies/mL for at least 1 year before screening and at screening.
- Participants had CD4 counts ≥450 cells/mm3 for at least 6 months prior to screening and had nadir CD4 counts ≥200 cells/mm3 since HIV diagnosis.4
Selected Study Results: Results presented at CROI 2023 and IAS 2023 showed that the combination of HTI vaccines with 10 doses of vesatolimod was safe with only one serious adverse event (SAE) reported, which was unrelated to the study drugs. HTI vaccines given with vesatolimod proved to be highly immunogenic. Vaccine-induced HTI-specific T-cell responses contributed to improved viral outcomes after participants underwent an analytical treatment interruption (ATI) of ART.13,14
Study Identifiers: GS-US-382-5445; NCT05281510
Sponsor: Gilead Sciences
Phase: 2a
Status: This study is ongoing, but not recruiting participants.
Study Purpose: The purpose of this open-label trial is to evaluate the safety and tolerability of the bNAbs VRC07-523LS and CAP256V2LS in combination with vesatolimod in early ART-treated women with clade C HIV.
Study Population:
- Participants are adult females with HIV who are recruited from the Females Rising through Education, Support, and Health (FRESH) acute HIV infection cohort.
- Participants have been receiving ART for at least 12 consecutive months prior to screening.
- Participants have HIV RNA <50 copies/mL at screening and have had HIV RNA <50 copies/mL for 12 consecutive months prior to screening. Participants have CD4 counts ≥500 cells/mm3.
- Participants have documented viral sensitivity to VRC07-523LS or CAP256V2LS.5
Additional early-phase trials evaluating vesatolimod for HIV treatment have been conducted, including:
- GS-US-382-1450 (NCT02858401): A Phase 1b dose-escalation study that evaluated the safety and virologic effect of vesatolimod in adults with HIV who had viral suppression on ART. This study has been completed, and results are published in Clin Infect Dis (2021).15
- GS-US-382-3961 (NCT03060447): A Phase 1b study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of vesatolimod in adults with HIV who had undetectable or low viral load levels (between 50 and 5,000 copies/mL) before initiating ART and viral suppression on ART. This study has been completed, and results are available from Sci Transl Med (2021) and CROI 2023.16
Adverse Events
AELIX-003 (NCT04364035)
In this Phase 2a trial, the combination of HTI vaccines and vesatolimod was safe. One participant had an SAE, which was deemed unrelated to the study drugs. No cases of cytokine-release syndrome were reported.4,13
GS-US-382-1450 (NCT02858401)
In this Phase 1b dose-escalation trial, 48 participants received multiple doses of either vesatolimod (1 to 12 mg) (n = 36) or placebo (n = 12) administered once every other week. At least one adverse event (AE) occurred in 64% of participants who received vesatolimod and 75% of participants who received placebo. AEs related to vesatolimod treatment included fatigue, headache, myalgia, and pyrexia. Drug-related AEs occurred more frequently in the 8-mg and 10/12-mg vesatolimod dose groups compared to the placebo group. Study drug-related AEs were mild, resolved within 1–2 days, and did not occur with each dose. There were no drug-related SAEs or discontinuations due to an AE. The majority of laboratory abnormalities that occurred during the study were Grade 1 or 2.3
GS-US-382-3961 (NCT03060447)
In this Phase 1b trial, 25 participants were randomized to receive 10 doses of vesatolimod (4 to 8 mg) (n = 17) or placebo (n = 8) administered once every other week. Ninety-four percent of participants receiving vesatolimod and 75% of participants receiving placebo had at least one AE, most of which were mild to moderate in severity. Drug-related AEs occurred in 53% of participants in the vesatolimod group and 13% of participants in the placebo group. The majority of AEs related to vesatolimod were mild, transient, influenza-like symptoms — chills, headache, lymphadenopathy, fatigue, and pyrexia. One participant receiving vesatolimod experienced a Grade 2 treatment-emergent SAE — chronic gastritis. Another participant receiving vesatolimod had Grade 3 drug-related cases of gout, arthralgia, and sciatica, all of which resolved without treatment. There were no discontinuations due to drug-related AEs. Laboratory abnormalities were mostly Grade 1 or 2 in severity.7
Drug Interactions
Drug-drug interactions associated with vesatolimod are currently unknown.
References
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem compound summary for CID 46241268, vesatolimod. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Gilead Sciences website. Pipeline. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Riddler SA, Para M, Benson CA, et al. Vesatolimod, a toll-like receptor 7 agonist, induces immune activation in virally suppressed adults living with human immunodeficiency virus–1. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;72(11):e815-e824. doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1534. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Aelix Therapeutics. A Phase IIa randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of HIV-1 vaccines MVA.HTI and ChAdOx1.HTI with TLR7 agonist vesatolimod (GS-9620) in early treated HIV-1 infection. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Registered on March 5, 2020. NLM Identifier: NCT04364035. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Gilead Sciences. A Phase 2a study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of a regimen of dual anti-HIV envelope antibodies, VRC07-523LS and CAP256V2LS, in a sequential regimen with a TLR7 agonist, vesatolimod, in early antiretroviral-treated HIV-1 clade C-infected women. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Registered on March 7, 2022. NLM Identifier: NCT05281510. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Tsai A, Irrinki A, Kaur J, et al. Toll-like receptor 7 agonist GS-9620 induces HIV expression and HIV-specific immunity in cells from HIV-infected individuals on suppressive antiretroviral therapy. J Virol. 2017;91(8):e02166-16. doi:10.1128/JVI.02166-16. Accessed October 30, 2024
- SenGupta D, Brinson C, DeJesus E, et al. The TLR7 agonist vesatolimod induced a modest delay in viral rebound in HIV controllers after cessation of antiretroviral therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2021;13(599):eabg3071. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abg3071. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Bam RA, Hansen D, Irrinki A, et al. TLR7 agonist GS-9620 is a potent inhibitor of acute HIV-1 infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;61(1):e01369-16. doi:10.1128/AAC.01369-16. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Rebbapragada I, Birkus G, Perry J, Xing W, Kwon H, Pflanz S. Molecular determinants of GS-9620-dependent TLR7 activation. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(1):e0146835. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0146835. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Lim SY, Osuna CE, Hraber PT, et al. TLR7 agonists induce transient viremia and reduce the viral reservoir in SIV-infected rhesus macaques on antiretroviral therapy. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(439):eaao4521. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aao4521. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Del Prete GQ, Alvord WG, Li Y, et al. TLR7 agonist administration to SIV-infected macaques receiving early initiated cART does not induce plasma viremia. JCI Insight. 4(11):e127717. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.127717. Accessed October 30, 2024
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID). A Phase I/IIa randomized, placebo-controlled trial of conserved-mosaic T-cell vaccine in a regimen with vesatolimod and broadly neutralizing antibodies in adults initiated on suppressive antiretroviral therapy during acute HIV-1. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Registered on September 5, 2023. NLM Identifier: NCT06071767. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Mothe B, Curran A, de Quirós JCLB, et al. A placebo-controlled randomized trial of the HTI immunogen vaccine and vesatolimod. Poster presented at: Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI); February 19-22, 2023; Seattle, WA. Poster 433. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Mothe B, Bailon L, Curran A, et al. T-cell responses induced by HTI vaccines and vesatolimod correlate with improved control of HIV rebound. Abstract presented at: International AIDS Society (IAS) Conference on HIV Science; July 23-26, 2023; Brisbane, Australia. Abstract LBEPB20. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Gilead Sciences. A Phase 1b, randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled dose-escalation study of the safety and biological activity of GS-9620 in HIV-1 infected, virologically suppressed adults. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Registered on July 26, 2016. NLM Identifier: NCT02858401. Accessed October 30, 2024
- Gilead Sciences. A Phase 1b, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of GS-9620 in antiretroviral treated HIV-1 infected controllers. In: ClinicalTrials.gov. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Registered on February 17, 2017. NLM Identifier: NCT03060447. Accessed October 30, 2024
Last Reviewed: October 30, 2024